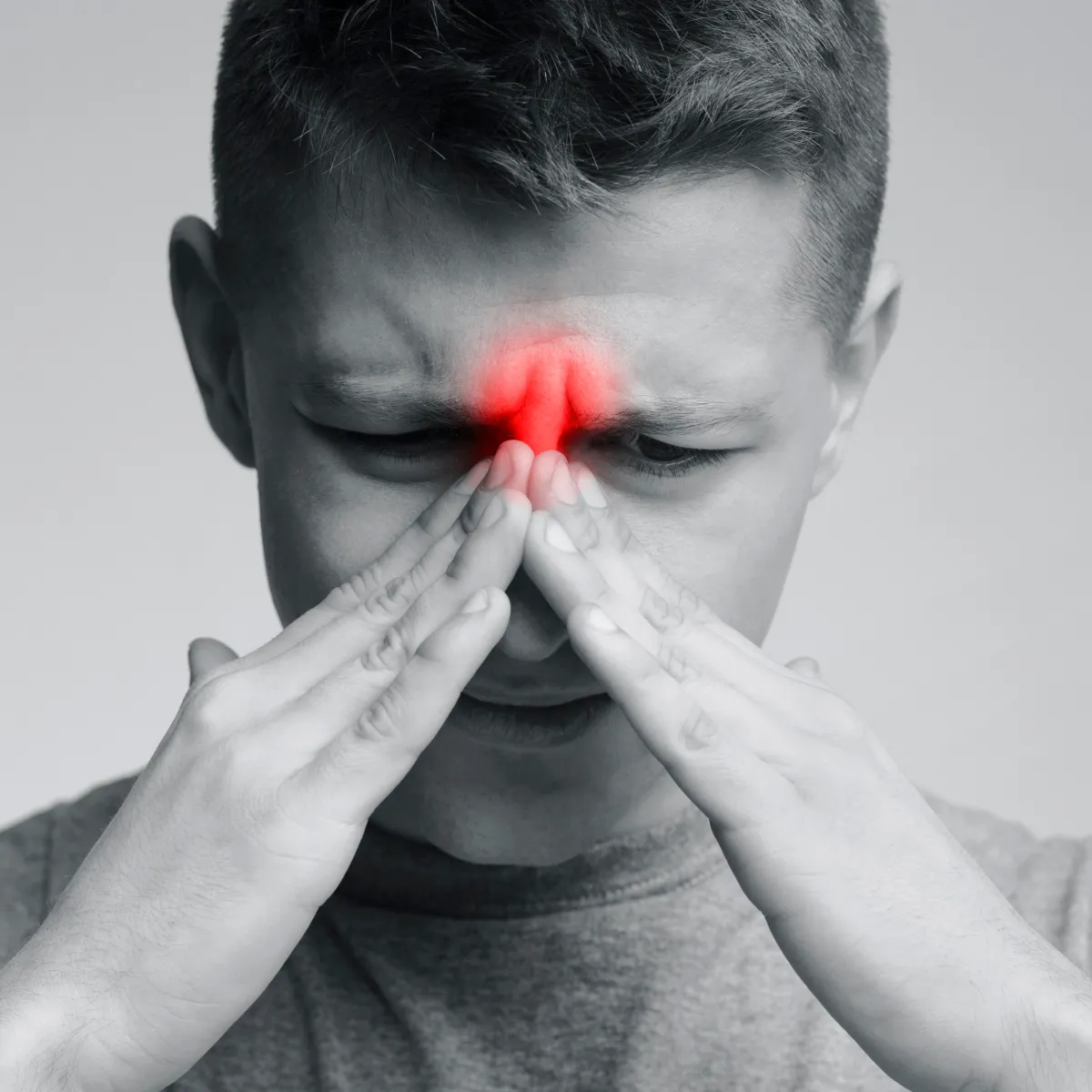
Serving The Lakeland Community Since 2002
Relieve Discomfort and Get Back Your Quality Of Life
Ear, Nose & Throat Care For Adults & Children Over 6 months
5420 Strickland Ave, Lakeland, FL 33812
Located In Hickman Office Park
Mon-Thu | 8:30am - 4:30pm
Fri | 8:30am - 12:00pm
Are Your Allergies Causing Discomfort?
Do You Have An Ear Infection?
- Experiencing Recurring Tonsil Or Throat Infections?
Are You Suffering From Irritability?
- Found Lumps Or Nodules On Your Neck Or Thyroid?
- Tired of your CPAP & looking for a surgical alternative?
Are You Experiencing possible polyps or nodules on the vocal cords?
Ear
Your ears enable you to experience many beautiful things in life such as great music, voices of loved ones, sounds of nature, and other great aspects of sound. Proper care is important to treating ear infections or discomfort which can be frustrating to deal with and can affect how you conduct your daily life.
Nose
Your nose helps filter out harmful allergens, allows you to breathe easily, take in the scent of home cooked meals, and add to the experience of outdoor adventures. Keeping your senses in good shape and reducing symptoms of allergies helps you stay happy and able to enjoy the big and small moments life has to offer.
Throat
Your neck and throat health are essential to staying comfortable in your daily life. You may not even think much about these parts of your body on a daily basis until an issue like recurring infections or nodules of the throat, thyroid, or vocal cords makes it uncomfortable to sleep, breathe, talk, or sing.
There's A Treatment That's Right For You
Ear, Nose
& Throat Care
Expert care and treatment for conditions & infections causing discomfort to the ears, nose, or throat.
Neck &
Head Care
Analysis and treatment for skin tumors on the head and neck and other related conditions.
Allergy Treatment & Management
Treatment with the goal of reducing the symptoms of allergies and make them less noticeable or dangerous.
Treatment For
Sleep Apnea
Treatment for sleep apnea disorder that make it easier to sleep, breathe while asleep, and get restful sleep.
We understand that living discomfort can be burdensome.
We've been helping families like yours for over 20 Years.
We Save Money For Families By Providing Effective Treatment & Preventing Long Term Damage
Our Practice Has Been Serving The Community Since 2002
Thousands Of Patients Have Seen Results From Treatment
Getting Started Is Easy
Make An
Appointment
Receive
Treatment
Schedule A
Follow Up
Get Your
Life Back
Helpful Resources

Understanding Parathyroid Disease
Understanding Parathyroid Disease
Introduction
The parathyroid glands may be small, but their role in regulating the body's calcium balance is monumental. These four tiny glands, located behind the thyroid, are essential for maintaining optimal calcium levels in the bloodstream. Proper calcium regulation is vital not only for bone strength but also for muscle function, nerve signaling, and heart health. When these glands malfunction, the consequences can be significant, affecting everything from bone density to cognitive function.
Parathyroid disease occurs when one or more of these glands become overactive (hyperparathyroidism) or underactive (hypoparathyroidism). The impact can range from subtle symptoms, like muscle weakness and fatigue, to severe issues like kidney stones and bone fractures.
The importance of early detection and treatment cannot be overstated. If left untreated, parathyroid disease can lead to chronic health issues like osteoporosis, cardiovascular complications, and persistent kidney problems. Treatment options range from lifestyle adjustments and monitoring to minimally invasive surgery.
Unlike other health conditions that may have obvious symptoms, parathyroid disease can be silent for a long time, often going unnoticed. However, subtle signs like muscle weakness, forgetfulness, and changes in mood can signal a deeper problem. Awareness of these indicators is essential, as early treatment can significantly reduce the likelihood of long-term complications. By recognizing the signs and seeking prompt medical advice, individuals can better protect their health and well-being.
Through this blog, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of parathyroid disease, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Our goal is to empower patients with the knowledge they need to seek proper care and improve their overall well-being.
What Are the Parathyroid Glands?
The parathyroid glands are four small, rice-sized glands located on the back of the thyroid gland in the neck. Despite their name, they are not related to the thyroid gland. Their primary function is to regulate calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood and bones through the production of parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH ensures that calcium is absorbed from food, released from bones, and retained by the kidneys.
Why Is Calcium Important?
Calcium is essential for:
Bone Strength: It provides structural integrity to bones and teeth.
Muscle Function: Calcium plays a vital role in muscle contraction, including heart function.
Nerve Signaling: Proper calcium levels ensure smooth communication between nerve cells.
Blood Clotting: Calcium is necessary for blood clot formation.
When calcium levels are not properly regulated, health issues such as kidney stones, weakened bones, and cognitive disturbances can occur.
Misconceptions About Parathyroid Glands
Many people mistakenly believe that parathyroid glands influence metabolism, like the thyroid. However, their only function is to regulate calcium. Understanding this distinction is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Unique Characteristics of Parathyroid Glands
Unlike most glands in the body, the parathyroid glands operate with a high degree of independence. Each of the four glands can function on its own, meaning that even if one gland malfunctions, the others continue to regulate calcium. This independence can be a double-edged sword, as it allows for redundancy but also increases the chances that one gland may become overactive or underactive.
What Happens When the Parathyroid Glands Malfunction?
When one or more parathyroid glands become overactive, a condition called primary hyperparathyroidism occurs. This results in the overproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH), causing calcium levels in the blood to rise (hypercalcemia). On the other hand, if the glands produce too little PTH, a condition called hypoparathyroidism occurs, leading to low calcium levels (hypocalcemia). Both conditions can lead to significant health problems if not addressed.
By understanding the role of the parathyroid glands and the potential for malfunction, individuals are better equipped to recognize symptoms and seek medical attention early. This knowledge is vital for maintaining long-term bone, nerve, and cardiovascular health.
Types of Parathyroid Disease
Parathyroid disease encompasses several disorders related to abnormal PTH production. Each type has distinct causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Primary hyperparathyroidism occurs when one or more parathyroid glands produce too much PTH, typically due to a benign tumor called a parathyroid adenoma. This overproduction leads to elevated calcium levels (hypercalcemia), resulting in symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, and kidney stones. If left untreated, primary hyperparathyroidism can increase the risk of osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and kidney dysfunction. Treatment often involves surgery to remove the affected gland. Some patients may experience muscle weakness and brain fog, both of which can improve significantly after treatment.
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
Secondary hyperparathyroidism occurs when the glands overproduce PTH in response to low blood calcium levels, often caused by chronic kidney disease or severe vitamin D deficiency. Unlike primary hyperparathyroidism, this form involves all four glands and requires addressing the underlying condition. Patients with chronic kidney disease frequently experience secondary hyperparathyroidism, which may require a combination of medication, dietary changes, and treatment for kidney health. Regular monitoring and blood tests are essential to manage calcium and phosphorus balance.
Tertiary Hyperparathyroidism
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism occurs when secondary hyperparathyroidism persists for an extended period, leading to permanent overactivity of the parathyroid glands. Even after the initial cause (like kidney disease) is addressed, the glands may continue to produce excess PTH. Tertiary hyperparathyroidism typically requires surgical intervention to remove the overactive glands. This condition is more common in patients undergoing long-term dialysis, and surgical intervention is often the only permanent solution.
Hypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism happens when the parathyroid glands produce too little PTH, leading to low calcium levels (hypocalcemia). This condition is often caused by surgical removal or accidental damage to the parathyroid glands during thyroid or neck surgery. It can also result from genetic disorders or autoimmune diseases. Symptoms include muscle cramps, tingling sensations, and, in severe cases, seizures. Treatment typically involves long-term calcium and vitamin D supplementation to maintain healthy calcium levels. Patients with chronic hypoparathyroidism may experience brittle nails, dry skin, and cognitive difficulties due to prolonged calcium deficiency.
Parathyroid Carcinoma
Parathyroid carcinoma is an extremely rare but serious form of parathyroid disease. Unlike other parathyroid disorders, parathyroid carcinoma is cancerous, and it causes severe hypercalcemia. Patients may experience extreme fatigue, persistent nausea, excessive thirst, and weight loss. Treatment requires surgical removal of the cancerous gland, often followed by additional cancer treatments like radiation or chemotherapy if necessary. Unlike benign forms of parathyroid disease, carcinoma requires long-term follow-up to ensure cancer does not recur.
Comparing the Types of Parathyroid Disease
While primary, secondary, and tertiary hyperparathyroidism all involve excess PTH production, their causes are different. Primary hyperparathyroidism is caused by a single gland malfunctioning, while secondary hyperparathyroidism results from underlying conditions like kidney disease. Tertiary hyperparathyroidism is a progression of secondary hyperparathyroidism, where the glands remain overactive even after the initial cause is addressed. Hypoparathyroidism, in contrast, is the only form that results in low PTH production. Understanding these distinctions can help patients identify symptoms early and seek appropriate treatment.
Understanding these different types of parathyroid disease highlights the importance of proper diagnosis and treatment. Each form of the disease presents unique challenges, but early intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes and prevent severe complications.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Symptoms of parathyroid disease can be subtle at first but worsen as calcium levels become more imbalanced. Symptoms vary depending on whether the disease involves too much (hyperparathyroidism) or too little (hypoparathyroidism) PTH production.
Symptoms of Hyperparathyroidism
Persistent Fatigue: Unexplained fatigue and low energy levels.
Bone Pain: Calcium depletion in bones can cause persistent aches and pains.
Frequent Urination: High calcium can strain the kidneys, increasing urination.
Kidney Stones: Excess calcium in the blood can form crystals in the kidneys.
Cognitive Issues: "Brain fog," confusion, or memory issues are common.
Abdominal Pain: High calcium levels can lead to digestive distress and stomach pain.
Muscle Weakness: People with hyperparathyroidism may experience general muscle weakness, particularly in the legs and arms.
Depression and Anxiety: Changes in calcium levels can affect mood and lead to anxiety, irritability, or depression.
Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty sleeping or frequent nighttime waking due to calcium imbalance.
Nausea and Vomiting: Digestive issues related to high calcium can cause nausea and vomiting.
Joint and Muscle Stiffness: Stiffness in joints and muscles can result from prolonged calcium imbalance.
Loss of Appetite: Elevated calcium can cause a persistent loss of appetite, leading to weight loss.
Symptoms of Hypoparathyroidism
Muscle Spasms: Sudden, painful muscle cramps, often in the hands, feet, or face.
Tingling Sensations: Numbness or tingling, especially around the mouth or extremities.
Hair and Nail Changes: Brittle nails and hair loss may occur with chronic calcium deficiency.
Seizures: In severe cases, hypocalcemia can lead to seizures or convulsions.
Heart Irregularities: Low calcium levels can disrupt heart rhythms, leading to arrhythmias.
Mental Health Changes: Patients may experience brain fog, confusion, and memory loss.
Difficulty Swallowing: Muscle spasms in the throat may lead to swallowing difficulties.
Dry Skin: Chronic hypocalcemia can result in dry, flaky skin.
Voice Changes: Hypocalcemia can affect the vocal cords, leading to a hoarse voice.
Facial Twitching: Uncontrolled twitching in the face, particularly around the eyes or mouth.
Patient Scenario
Sarah, a 45-year-old teacher, experienced fatigue, joint pain, and frequent kidney stones for years before seeking help. Blood tests revealed elevated calcium and PTH levels, confirming primary hyperparathyroidism. After surgery, Sarah's energy returned, and her kidney stone issues resolved.
In another case, Mark, a 62-year-old retired construction worker, experienced severe cramps in his hands and face, along with unusual tingling sensations around his mouth. Blood tests revealed low calcium and low PTH, confirming hypoparathyroidism. After treatment with calcium and vitamin D supplements, Mark's symptoms improved, and he regained full muscle control.
In a third case, Lisa, a 37-year-old marketing executive, struggled with sleep disturbances, brain fog, and a general sense of anxiety. After visiting multiple specialists, she finally had her PTH and calcium levels tested. The results showed she had mild primary hyperparathyroidism. After undergoing minimally invasive parathyroid surgery, her sleep improved, and she reported feeling mentally sharper than she had in years.
In a fourth case, James, a 50-year-old landscaper, began experiencing persistent nausea and vomiting. His appetite decreased, and he lost 15 pounds within a few months. His doctor ordered blood tests and imaging studies, revealing an overactive parathyroid gland. After surgery to remove the overactive gland, James's symptoms resolved, and his appetite returned to normal.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing parathyroid disease requires multiple diagnostic tools to pinpoint the exact cause. Early detection is essential for effective treatment, as untreated parathyroid disease can lead to long-term health complications such as kidney stones, osteoporosis, and neurological issues.
Blood Tests
A blood test is the first step in diagnosing parathyroid disease. It measures calcium, parathyroid hormone (PTH), and vitamin D levels. Elevated calcium and PTH levels often point to primary hyperparathyroidism, while low calcium and PTH levels suggest hypoparathyroidism. Blood tests may also assess kidney function and phosphorus levels to rule out secondary hyperparathyroidism, which is linked to chronic kidney disease.
24-Hour Urine Collection
In some cases, doctors may order a 24-hour urine collection to assess how much calcium is being excreted. This helps distinguish between familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH) and primary hyperparathyroidism. While both conditions can result in high calcium levels, FHH typically shows low calcium excretion, whereas hyperparathyroidism leads to elevated calcium excretion.
Imaging Studies
Imaging tests help locate abnormal parathyroid glands that may require surgery. Common imaging techniques include:
Sestamibi Scan: This nuclear medicine scan identifies hyperactive parathyroid glands using a small amount of radioactive material.
Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the neck, often used to locate parathyroid adenomas.
CT Scan (4D-CT): A specialized CT scan that captures 3D images over time, making it easier to pinpoint overactive parathyroid glands.
These imaging tests are particularly useful when planning for minimally invasive parathyroid surgery, as they help surgeons locate the exact gland that needs to be removed.
Bone Density Tests
Bone density tests measure bone strength and help identify signs of osteoporosis or osteopenia. Patients with untreated hyperparathyroidism may experience a loss of bone density, increasing the risk of fractures. The most common test is the dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan, which measures bone density in the hip, spine, and wrist.
Genetic Testing
If doctors suspect a genetic cause for parathyroid disease, they may recommend genetic testing. This is especially relevant for patients with a family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN), which increases the likelihood of parathyroid tumors. Identifying genetic mutations can inform treatment decisions and screening for other endocrine-related conditions.
Summary of the Diagnosis Process
Diagnosing parathyroid disease is a multi-step process involving blood tests, imaging, urine collection, and, in some cases, genetic testing. Accurate diagnosis is critical for determining the most effective treatment plan. Early intervention can prevent complications like bone loss, cognitive issues, and kidney stones. If you suspect parathyroid disease, speak with a healthcare provider to begin the diagnostic process as soon as possible.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for parathyroid disease depend on the specific type of disorder diagnosed. The goal of treatment is to restore calcium balance in the body, relieve symptoms, and prevent long-term complications such as kidney stones, bone loss, and cardiovascular issues. Here are the most common treatment approaches for parathyroid disease.
Minimally Invasive Parathyroidectomy
For primary hyperparathyroidism, the most effective treatment is a minimally invasive parathyroidectomy (MIP). During this procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision in the neck and uses imaging guidance to locate and remove the overactive parathyroid gland. This approach offers several benefits, including:
Reduced Recovery Time: Most patients return home the same day.
Smaller Incision: Minimal scarring compared to traditional surgery.
Higher Accuracy: Surgeons use imaging studies like sestamibi scans and 4D-CTs to pinpoint the gland that needs removal.
Minimally invasive parathyroidectomy has a high success rate, with most patients experiencing immediate relief from symptoms like fatigue, bone pain, and mental fog.
Traditional Parathyroid Surgery
In cases where multiple parathyroid glands are overactive, such as secondary or tertiary hyperparathyroidism, traditional parathyroid surgery may be necessary. Unlike minimally invasive surgery, this procedure requires a larger incision, and the surgeon may remove more than one gland. While recovery is longer, it is often the best option for patients with extensive parathyroid disease or multiple affected glands.
Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation
For hypoparathyroidism, where the parathyroid glands do not produce enough PTH, treatment typically involves daily calcium and vitamin D supplements. Since the body is not receiving the natural regulation from PTH, these supplements help maintain calcium balance in the blood. Patients may also receive prescription-strength versions of calcitriol, a more active form of vitamin D, to enhance calcium absorption. Long-term monitoring is essential to prevent complications like kidney calcification from excess calcium.
Recombinant PTH Therapy
In some cases of chronic hypoparathyroidism, patients may be prescribed recombinant parathyroid hormone (PTH 1-84). This injectable medication mimics the body's natural PTH, helping to better regulate calcium levels. This therapy is typically reserved for patients who do not respond well to calcium and vitamin D supplements alone. It provides better control of calcium levels and reduces the risk of kidney issues caused by prolonged calcium supplementation.
Medications for Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
For secondary hyperparathyroidism, which is often caused by chronic kidney disease, treatment focuses on addressing the underlying condition. Common approaches include:
Phosphate Binders: Reduce phosphate absorption from food to prevent overproduction of PTH.
Calcimimetics (like Cinacalcet): These drugs reduce PTH production by making the parathyroid glands more sensitive to calcium.
Vitamin D Analogs: Used to raise blood calcium levels and reduce PTH secretion.
Medications are typically prescribed alongside dietary changes to manage calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D levels in the body. This approach reduces symptoms like bone pain, itching, and cardiovascular complications associated with prolonged secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Patients with mild parathyroid disease may be advised to make lifestyle changes as part of a “watch and wait” approach. Lifestyle recommendations include:
Dietary Changes: Eating more calcium-rich foods (for hypoparathyroidism) or limiting dietary calcium (for hyperparathyroidism) based on the type of disease.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps prevent kidney stones, especially in patients with high blood calcium levels.
Exercise: Weight-bearing exercises strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures caused by bone loss.
Lifestyle changes are often recommended in combination with other treatments to achieve long-term calcium balance.
Summary of Treatment Options
Treatment for parathyroid disease varies significantly based on the specific disorder. While some patients may benefit from lifestyle changes and medication, others require surgery to resolve the condition permanently. Minimally invasive parathyroidectomy is considered the gold standard for primary hyperparathyroidism, offering quick recovery and effective symptom relief. Patients with secondary or tertiary hyperparathyroidism often require more extensive surgery or a combination of medications and lifestyle adjustments. For hypoparathyroidism, long-term calcium and vitamin D management is essential to prevent complications. Working closely with a healthcare provider ensures the best treatment approach for each individual’s needs.
Conclusion
Parathyroid disease, while often overlooked, can have a profound impact on a person's health. The role of the parathyroid glands in regulating calcium is critical for maintaining strong bones, proper muscle function, and optimal nerve signaling. When these glands malfunction, the effects can be felt in nearly every part of the body, from the kidneys to the brain. This makes early diagnosis and treatment essential for long-term health and well-being.
One of the most effective treatments for primary hyperparathyroidism is minimally invasive parathyroidectomy (MIP), which has a high success rate and provides fast relief from symptoms like fatigue, brain fog, and joint pain. Patients often experience noticeable improvements in their energy levels, mental clarity, and physical comfort within days of the procedure. For those with secondary or tertiary hyperparathyroidism, treatment may require a more comprehensive approach involving lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, surgery.
For individuals with hypoparathyroidism, ongoing management is essential. This includes daily calcium and vitamin D supplementation to prevent complications like muscle spasms, seizures, and cognitive issues. Patients may also benefit from recombinant parathyroid hormone (PTH) therapy, which can provide more stable calcium control. Working closely with a healthcare provider is key to maintaining health and preventing long-term complications.
The earlier parathyroid disease is detected, the better the outcome. Many people live with symptoms like fatigue, muscle pain, and cognitive fog without realizing that a parathyroid problem could be the root cause. Raising awareness about these signs can lead to earlier intervention and a higher quality of life for patients. If you or a loved one suspects they may have parathyroid disease, consult with a healthcare provider to get the proper diagnosis and begin appropriate treatment. Taking action now can prevent long-term complications and lead to a healthier, more active life.
Family Care Ear, Nose & Throat Physician

Dr. Herman Matallana, DO
Otolaryngology Specialist
Dr. Herman Matallana, known by his patients as Dr. Mat, is a dedicated physician with over ten years of experience in the treatment of Ear, Nose and Throat, Reconstructive Surgery and Allergies. Dr. Mat graduated from Kansas City University of Medicine and Bio-Sciences and did his specialization in Otolaryngology, Head & Neck and Reconstructive Surgery at Des Peres Hospital in St. Louis, MO.
What Our Clients Are Saying
What Our Clients
Are Saying

Dr Mat is a great doctor. He is attentive, caring, and best of all he listens to your concerns. His staff are all very polite, respectful and attentive to your needs. This is a doctor's office that work together as a team and they all know without a doubt what's going with each patient. Imñam very grateful that I was referred to Dr Mat.
Brenda B.
★ ★ ★ ★ ★

Dr Mat is AMAZING! He takes time to listen to your concerns and answer questions. My surgery was at Bartow Medical Center. The amount of respect the nurses and other staff members have for Dr Mat shows tremendously. They were amazing and they took phenomenal care of me.
Kylie S.
★ ★ ★ ★ ★

Dr. Matallana has been nothing but amazing for myself and my children. From tubes all the way to reconstructive surgery on my eldest child's nose. Outstanding doctor, outstanding care.
Jess W.
★ ★ ★ ★ ★

Receive Care & Improve Your Quality Of Life
Finding the right ENT practice to care for your family can be challenging and more frustrating than it needs to be.
We make sure every patient receives the care they need by doing a comprehensive evaluation and putting together an effective treatment plan.
At Family Care ENT we know that your family's health and comfort is your top priority. The problem is not all practices provide the same level of care, expertise, and experience.
We believe in giving the highest standard of care in order to improve your health. We understand recurring infections, severe allergies, nodules, and sleep apnea can be frustrating or intimidating which is why we've been helping people just like you for over 20 years find the perfect treatment plans.
Here's how we do it:
1. Make An Appointment
2. Receive Treatment
3. Schedule A Follow-Up
4. See Results
So, schedule an appointment today so you can stop living with irritation or discomfort and start your path to relief instead.
What Are My Options?
Option 1
You could wait to see if the problem self resolves and risk the condition worsening or permanent damage.
Option 2
You could attempt to treat the condition yourself with over the counter medication.
(this may work for people who are medical professionals and are great at determining proper treatments.)
Option 3
You could make an appointment and we'll help you identify the most effective treatment for your needs specifically.